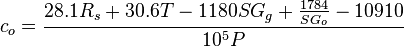Difference between revisions of "Vasquez and Beggs Oil Compressibility correlation"
From wiki.pengtools.com
(→Math & Physics) |
(→Solution) |
||
| (8 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 11: | Line 11: | ||
:<math>c_o = \frac{28.1R_s+30.6T-1180SG_g+\frac{1784}{SG_o}-10910}{10^5P}</math><ref name=PracticalPVT/> | :<math>c_o = \frac{28.1R_s+30.6T-1180SG_g+\frac{1784}{SG_o}-10910}{10^5P}</math><ref name=PracticalPVT/> | ||
| − | == Example. Calculation of the oil | + | == Example. Calculation of the oil compressibility == |
Example source <ref name=DW/> | Example source <ref name=DW/> | ||
===Input data=== | ===Input data=== | ||
:<math>R_s</math> = 53.24 sm<sup>3</sup>/sm<sup>3</sup> at P = 10 MPa | :<math>R_s</math> = 53.24 sm<sup>3</sup>/sm<sup>3</sup> at P = 10 MPa | ||
| + | :<math>T</math> = 90C or 363K | ||
:<math>SG_o</math> = 0.85 or 35 API | :<math>SG_o</math> = 0.85 or 35 API | ||
:<math>SG_g</math> = 0.75 | :<math>SG_g</math> = 0.75 | ||
| − | |||
| − | Calculate oil | + | Calculate oil compressibility at p = 10 MPa? |
===Solution=== | ===Solution=== | ||
| − | :<math> | + | :<math>c_o</math> = 0.002907 MPa<sup>-1</sup> or 2.95E-4 atm |
The solution is available in the online PVT calculator software model at [https://www.pengtools.com/pvtCalculator?paramsToken=de71e4cc29541ab2117e07408864410c www.pengtools.com] | The solution is available in the online PVT calculator software model at [https://www.pengtools.com/pvtCalculator?paramsToken=de71e4cc29541ab2117e07408864410c www.pengtools.com] | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
== Nomenclature == | == Nomenclature == | ||
| − | :<math> | + | :<math> c_o </math> = oil compressibility, MPa<sup>-1</sup> |
| + | :<math> P </math> = pressure, MPa | ||
:<math> R_s </math> = solution gas-oil ratio, sm<sup>3</sup>/sm<sup>3</sup> | :<math> R_s </math> = solution gas-oil ratio, sm<sup>3</sup>/sm<sup>3</sup> | ||
:<math> SG_g </math> = gas specific gravity, dimensionless | :<math> SG_g </math> = gas specific gravity, dimensionless | ||
:<math> SG_o </math> = oil specific gravity, dimensionless | :<math> SG_o </math> = oil specific gravity, dimensionless | ||
| − | :<math> | + | :<math> T </math> = temperature, °K |
| − | |||
== References == | == References == | ||
| Line 82: | Line 75: | ||
{{#seo: | {{#seo: | ||
| − | |title= | + | |title=Vasquez and Beggs Oil Compressibility correlation |
|titlemode= replace | |titlemode= replace | ||
| − | |keywords=oil | + | |keywords=oil compressibility, petroleum engineering, PVT |
| − | |description= | + | |description=Vasquez and Beggs correlation is an empirical correlation for the oil compressibility published in 1980 |
}} | }} | ||
Latest revision as of 07:21, 29 September 2020
Contents
Vasquez and Beggs Oil Compressibility correlation
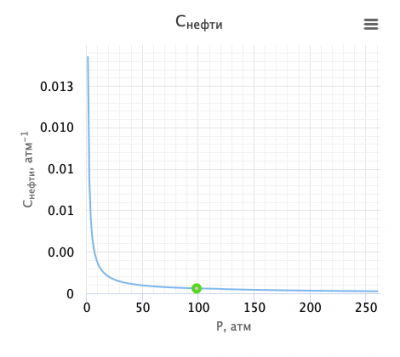
Vasquez and Beggs is an empirical correlation for the oil compressibility published in 1980[1].
Math & Physics
Example. Calculation of the oil compressibility
Example source [3]
Input data
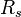 = 53.24 sm3/sm3 at P = 10 MPa
= 53.24 sm3/sm3 at P = 10 MPa = 90C or 363K
= 90C or 363K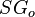 = 0.85 or 35 API
= 0.85 or 35 API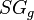 = 0.75
= 0.75
Calculate oil compressibility at p = 10 MPa?
Solution
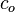 = 0.002907 MPa-1 or 2.95E-4 atm
= 0.002907 MPa-1 or 2.95E-4 atm
The solution is available in the online PVT calculator software model at www.pengtools.com
Nomenclature
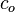 = oil compressibility, MPa-1
= oil compressibility, MPa-1 = pressure, MPa
= pressure, MPa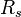 = solution gas-oil ratio, sm3/sm3
= solution gas-oil ratio, sm3/sm3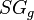 = gas specific gravity, dimensionless
= gas specific gravity, dimensionless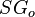 = oil specific gravity, dimensionless
= oil specific gravity, dimensionless = temperature, °K
= temperature, °K
References
- ↑
Vasquez, M.; Beggs, H.D. (1980). "Correlations for Fluid Physical Properties Prediction"
 . Journal of Petroleum Technology. Society of Petroleum Engineers. 32 (SPE-6719-PA).
. Journal of Petroleum Technology. Society of Petroleum Engineers. 32 (SPE-6719-PA).
- ↑ Afanasyev, Vitaliy; Moskvin, Igor; Wolcott, Ken; McCain, W.D. (2004). "Practical PVT Calculations for black oils". YUKOS publication.
- ↑
Wolcott, Don (2009). Applied Waterflood Field Development
 . Houston: Energy Tribune Publishing Inc.
. Houston: Energy Tribune Publishing Inc.