Difference between revisions of "Electrical Submersible Pump"
(→ESP Design Software) |
(→ESP Design Software) |
||
| (34 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | == | + | ==Electrical Submersible Pump== |
[[Electrical Submersible Pump]] ('''ESP''') is an artificial lift method to lift fluids from the wells. | [[Electrical Submersible Pump]] ('''ESP''') is an artificial lift method to lift fluids from the wells. | ||
| − | + | [[Electrical Submersible Pump|Electrical Submersible Pumps]] are used to pump off the oil wells and produce water from the water source wells. | |
| − | = | + | A typical submersible pumping unit consists of an electric motor, a seal section, an intake section, a multistage centrifugal pump, an electrical cable, a surface-installed switchboard, a junction box, and transformers <ref name = KermitBrown1984/>. |
| − | ESP | + | 750+ [[Electrical Submersible Pump | ESP]] models are grouped into the [[ESP catalog]]. |
| + | |||
| + | [[:Category:pumpDesign| Pump Design]] - [[Electrical Submersible Pump|ESP]] pump design software available online at [https://www.pengtools.com www.pengtools.com]. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==ESP Performance Curves== | ||
| + | |||
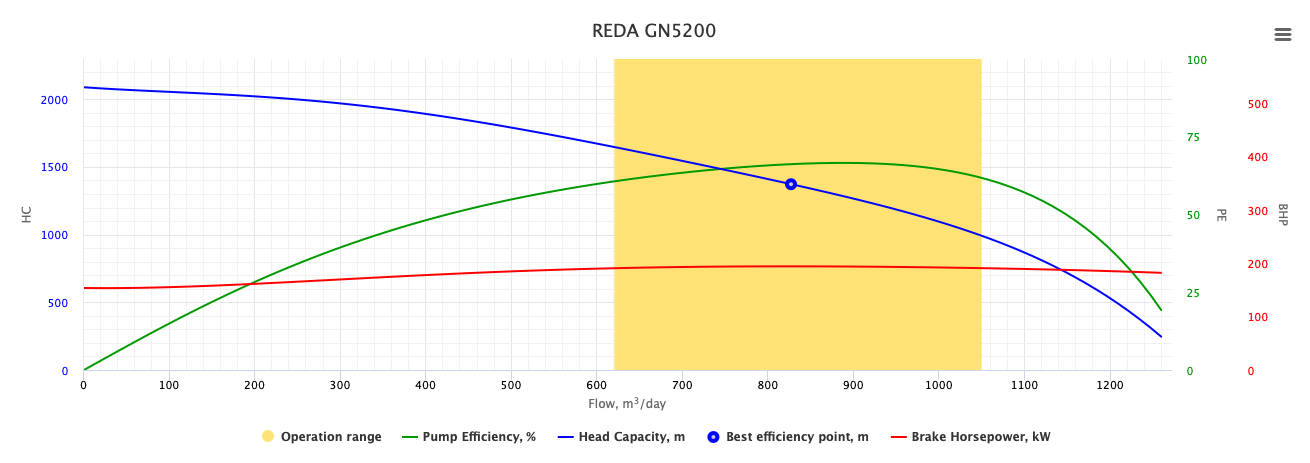
| + | The performance curves of ESP represent the relationship between flow rate capacity and: | ||
* Head capacity | * Head capacity | ||
* Pump efficiency | * Pump efficiency | ||
* Brake Horsepower | * Brake Horsepower | ||
| − | ESP | + | ESP Performance Curves also show Best Efficiency Point (BEP) and ESP operating range. |
| + | |||
| + | ESP Performance Curves are used for ESP design and sizing. | ||
| + | |||
| + | These curves are for a fixed power cycle i.e. 50Hz, and can be changed with variable frequency controllers. | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[File:ESP Diagram.png| Reda GN5200 ESP Performance Curves]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | <center>'''REDA GN5200 ESP Performance Curves''' for 150 stages - 60 Hz</center> | ||
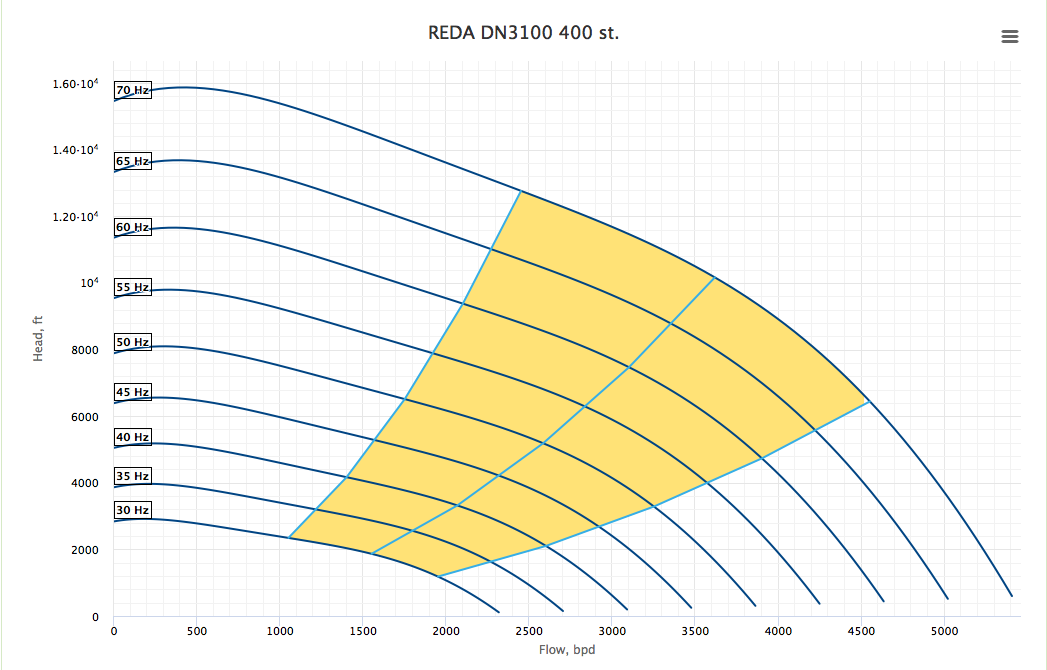
| − | ESP | + | ==ESP Tornado chart== |
| − | [[ | + | [[ESP Tornado chart]] is the variable-speed [[Electrical Submersible Pump| ESP]] performance chart showing the [[Electrical Submersible Pump| ESP]] performance curves at different frequencies. |
| − | <center>'''REDA | + | [[File:Tornadochart.png| Tornado chart for the REDA DN3100 pump with 400 stages]] |
| + | |||
| + | <center>[[ESP Tornado chart]] for the '''REDA DN3100''' pump with 400 stages</center> | ||
==ESP System== | ==ESP System== | ||
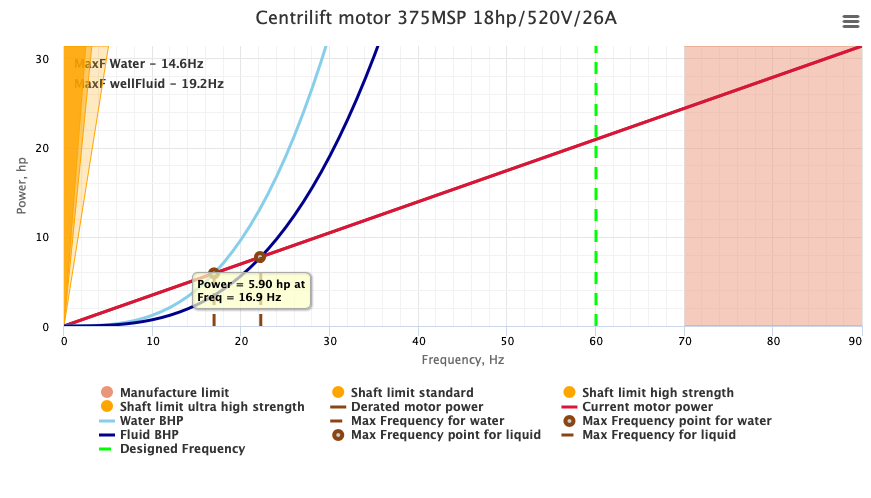
| − | + | ===ESP Motor=== | |
| − | + | [[File:ESP Motor.png| ESP Motor: Centrilift motor 375MSP 18hp/520V/26A]] | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | <center>ESP Motor: Centrilift motor 375MSP 18hp/520V/26A </center> | |
| + | |||
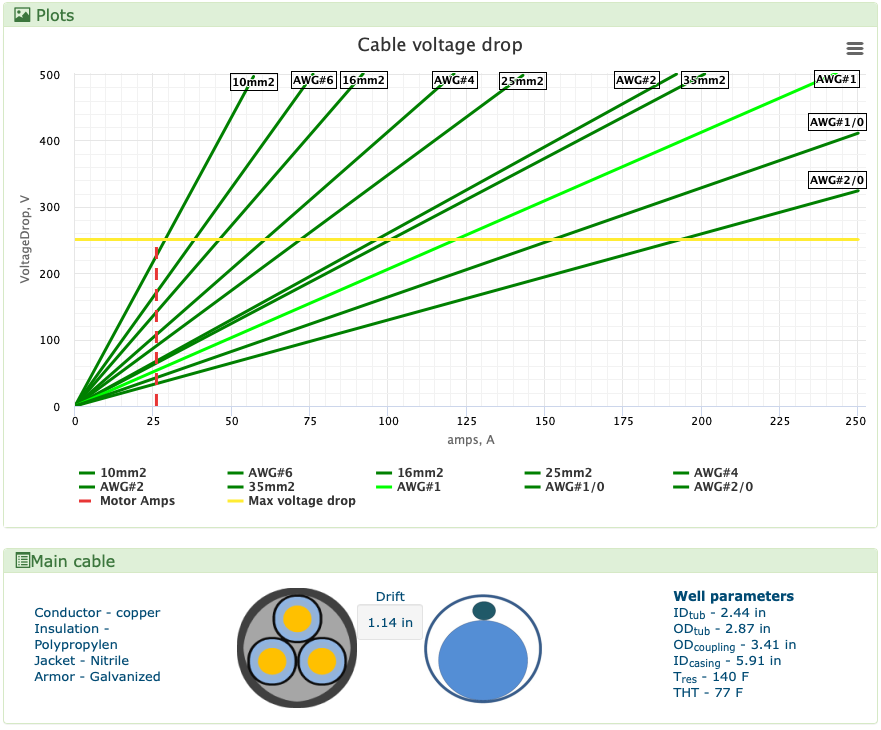
| + | ===ESP Cable=== | ||
| + | [[File:ESP Cable.png| ESP Cable: #1 AWG CPNR Centrilift 34.5/-/2.51kg/m SOL 5kV]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | <center>ESP Cable: #1 AWG CPNR Centrilift 34.5/-/2.51kg/m SOL 5kV</center> | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===ESP Drive=== | ||
| + | [[File:ESP Drive.png| ESP Drive]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | <center>ESP Drive </center> | ||
==ESP Design Software== | ==ESP Design Software== | ||
| − | * [[:Category:pumpDesign| | + | * [[:Category:pumpDesign| Pump Design]] - [[Electrical Submersible Pump|ESP]] pump design software available online at [https://www.pengtools.com www.pengtools.com]. |
* Subpump | * Subpump | ||
* Autograph PC | * Autograph PC | ||
| Line 37: | Line 63: | ||
* Prosper | * Prosper | ||
* SelPro | * SelPro | ||
| − | * RosPump | + | * RosPump / Роспамп |
* Автотехнолог | * Автотехнолог | ||
| Line 43: | Line 69: | ||
[[ESP catalog]]<BR/> | [[ESP catalog]]<BR/> | ||
[[ESP Tornado chart]] | [[ESP Tornado chart]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | == References == | ||
| + | <references> | ||
| + | <ref name= KermitBrown1984 >{{cite book | ||
| + | |last1= Brown |first1= Kermit | ||
| + | |title=The Technology of Artificial Lift Methods. Volume 4. Production Optimization of Oil and Gas Wells by Nodal System Analysis | ||
| + | |publisher=PennWellBookss | ||
| + | |date=1984 | ||
| + | |place=Tulsa, Oklahoma | ||
| + | }}</ref> | ||
| + | |||
| + | </references> | ||
[[Category:PumpDesign]] | [[Category:PumpDesign]] | ||
| Line 51: | Line 89: | ||
|titlemode= replace | |titlemode= replace | ||
|keywords=Electrical Submersible Pump | |keywords=Electrical Submersible Pump | ||
| − | |description= | + | |description=Electrical Submersible Pump is an artificial lift method to lift fluids from the wells. |
}} | }} | ||
Latest revision as of 09:38, 6 September 2022
Contents
Electrical Submersible Pump
Electrical Submersible Pump (ESP) is an artificial lift method to lift fluids from the wells.
Electrical Submersible Pumps are used to pump off the oil wells and produce water from the water source wells.
A typical submersible pumping unit consists of an electric motor, a seal section, an intake section, a multistage centrifugal pump, an electrical cable, a surface-installed switchboard, a junction box, and transformers [1].
750+ ESP models are grouped into the ESP catalog.
Pump Design - ESP pump design software available online at www.pengtools.com.
ESP Performance Curves
The performance curves of ESP represent the relationship between flow rate capacity and:
- Head capacity
- Pump efficiency
- Brake Horsepower
ESP Performance Curves also show Best Efficiency Point (BEP) and ESP operating range.
ESP Performance Curves are used for ESP design and sizing.
These curves are for a fixed power cycle i.e. 50Hz, and can be changed with variable frequency controllers.
ESP Tornado chart
ESP Tornado chart is the variable-speed ESP performance chart showing the ESP performance curves at different frequencies.
ESP System
ESP Motor
ESP Cable
ESP Drive
ESP Design Software
- Pump Design - ESP pump design software available online at www.pengtools.com.
- Subpump
- Autograph PC
- Pipesim ESP design
- DesignRite
- WellFlow
- Prosper
- SelPro
- RosPump / Роспамп
- Автотехнолог
See also
References
- ↑ Brown, Kermit (1984). The Technology of Artificial Lift Methods. Volume 4. Production Optimization of Oil and Gas Wells by Nodal System Analysis. Tulsa, Oklahoma: PennWellBookss.