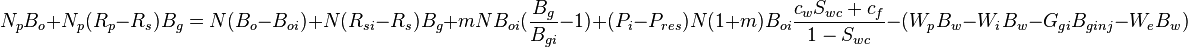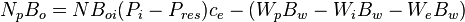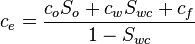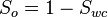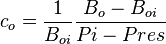Difference between revisions of "Oil Material Balance"
From wiki.pengtools.com
(→Math & Physics) |
(→Nomenclature) |
||
| (48 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 4: | Line 4: | ||
== Math & Physics == | == Math & Physics == | ||
| − | Equating all underground withdrawals to the sum of the volume changes: | + | Equating all underground withdrawals to the sum of the volume changes<ref name=DakeF />: |
| − | :<math>N_p | + | :<math>N_p B_o + N_p (R_p - R_s) B_g = N (B_o - B_{oi}) + N (R_{si} - R_s) B_g + m N B_{oi} (\frac{B_g}{B_{gi}} - 1) + (P_i - P_{res}) N (1 + m) B_{oi} \frac{c_w S_{wc} + c_f}{1 - S_{wc}}- (W_p B_w - W_i B_w - G_{gi} B_{ginj} - W_e B_w) </math> |
| − | Np * Bo + Np * (Rp - Rs) * Bg | + | For use in the code to find Pres: |
| + | Pres = Pi - (Np * Bo + Np * (Rp - Rs) * Bg + (Wp * Bw - Wi * Bw - Ggi * Bginj - We * Bw) - (N * (Bo - Boi) + N * (Rsi - Rs) * Bg + m * N * Boi * (Bg / Bgi - 1))) * (1 - Swc) / (N * (1 + m) * Boi * (cw * Swc + cf)) | ||
| − | + | For use in the code to find Np: | |
| − | :<math> | + | Np = (N * (Bo - Boi) + N * (Rsi - Rs) * Bg + m * N * Boi * (Bg / Bgi - 1) + N * (1 + m) * Boi * (Pi - Pres) * (cw * Swc + cf) / (1 - Swc) - (Wp * Bw - Wi * Bw - Gging * Bgi - We * Bw)) / (Bo + (Rp - Rs) * Bg) |
| + | |||
| + | === Above the bubble point === | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | :<math>N_p B_o = N B_{oi} (P_i - P_{res}) c_e - (W_p B_w - W_i B_w - W_e B_w) </math> | ||
| + | where | ||
| + | :<math>c_e = \frac{c_o S_o + c_w S_{wc} + c_f}{1 - S_{wc}}</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | :<math>S_o = 1 - S_{wc}</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | :<math>c_o = \frac{1}{B_{oi}} \frac{B_o-B_{oi}}{Pi - Pres}</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | == Discussion == | ||
| + | |||
| + | {{Quote| text = ... most powerful tool for investigating reservoirs and understanding their performance ... | source = L.P. Dake <ref name=DakeP />}} | ||
| + | |||
| + | {{Quote| text = ... the safest technique in the business since it's minimum assumption route through the subject of reservoir engineering ... | source = L.P. Dake <ref name=DakeP />}} | ||
== See also == | == See also == | ||
| − | [[ | + | [[Gas Material Balance]] <BR/> |
| + | [[Gas Flowing Material Balance]] <BR/> | ||
| + | [[Oil Flowing Material Balance]] <BR/> | ||
== Nomenclature == | == Nomenclature == | ||
| − | :<math> | + | :<math> B_{g}</math> = gas formation volume factor at Pres, bbl/scf |
| − | :<math> B_{ | + | :<math> B_{gi}</math> = initial gas formation volume factor, bbl/scf |
| − | :<math> | + | :<math> B_{ginj}</math> = injection gas formation volume factor at Pres, bbl/scf |
| − | :<math> | + | :<math>B_o</math> = oil formation volume factor at Pres, bbl/stb |
| + | :<math> B_{oi}</math> = initial oil formation volume factor, bbl/stb | ||
| + | :<math>B_w</math> = water formation volume factor at Pres, bbl/stb | ||
| + | :<math>c_e</math> = effective system compressibility at Pres, 1/psia | ||
| + | :<math>c_f</math> = formation compressibility at initial pressure and temperature, 1/psia | ||
| + | :<math>c_w</math> = water compressibility at Pres, 1/psia | ||
| + | :<math>G_{gi}</math> = gas injection volume, scf | ||
| + | :<math>G_p</math> = gas cumulative production volume, scf | ||
| + | :<math> HCPV_{gascap}</math> = initial gas cap hydrocarbon pore volume, bbl | ||
| + | :<math> HCPV_{oil}</math> = initial oil hydrocarbon pore volume, bbl | ||
| + | :<math> m = \frac{HCPV_{gascap}}{HCPV_{oil}}=\frac{S_g}{S_o}</math> , initial gas cap oil leg ratio, dimensionless | ||
| + | :<math> N </math> = stock tank oil initially in place, stb | ||
| + | :<math> N_p</math> = oil cumulative production volume, stb | ||
| + | :<math> P_i</math> = initial reservoir pressure, psia | ||
| + | :<math> P_{res}</math> = average reservoir pressure, psia | ||
| + | :<math> R_p = \frac{Gp}{Np}</math> , cumulative GOR, scf/stb | ||
| + | :<math> R_s</math> = solution oil-gas ratio, scf/bbl | ||
| + | :<math> R_{si} </math> = initial solution oil-gas ratio, scf/bbl | ||
| + | :<math> S_{g}</math> = initial gas saturation, fraction | ||
| + | :<math> S_{o}</math> = initial oil saturation, fraction | ||
| + | :<math> S_{wc}</math> = connate water saturation, fraction | ||
| + | :<math> W_e </math> = water influx volume, stb | ||
| + | :<math> W_i</math> = water injection volume, stb | ||
| + | :<math>W_p </math> = water production volume, stb | ||
== References == | == References == | ||
| Line 30: | Line 75: | ||
<ref name=DakeF>{{cite book | <ref name=DakeF>{{cite book | ||
|last1= Dake |first1=L.P. | |last1= Dake |first1=L.P. | ||
| − | |title=Fundamentals of | + | |title=Fundamentals of Reservoir Engineering |
|date=1978 | |date=1978 | ||
|publisher=Elsevier Science | |publisher=Elsevier Science | ||
|place=Amsterdam, Hetherlands | |place=Amsterdam, Hetherlands | ||
|isbn=0-444-41830-X | |isbn=0-444-41830-X | ||
| + | }}</ref> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <ref name=DakeP>{{cite book | ||
| + | |last1= Dake |first1=L.P. | ||
| + | |title=The Practice of Reservoir Engineering | ||
| + | |date=1994 | ||
| + | |publisher=Elsevier Science | ||
| + | |place=Amsterdam, Hetherlands | ||
| + | |isbn=0-444-88538-2 | ||
}}</ref> | }}</ref> | ||
| Line 41: | Line 95: | ||
[[Category:E&P Portal]] | [[Category:E&P Portal]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | {{#seo: | ||
| + | |title=Oil Material Balance | ||
| + | |titlemode= replace | ||
| + | |keywords=reservoir engineering, material balance, petroleum engineering, equation | ||
| + | |description=Oil Material Balance is the most powerful tool for investigating reservoirs and understanding their performance. | ||
| + | }} | ||
Latest revision as of 11:36, 20 April 2024
Contents
Brief
The general form of the Oil Material Balance equation was first published by Schilthuis in 1941[1].
Math & Physics
Equating all underground withdrawals to the sum of the volume changes[1]:
For use in the code to find Pres:
Pres = Pi - (Np * Bo + Np * (Rp - Rs) * Bg + (Wp * Bw - Wi * Bw - Ggi * Bginj - We * Bw) - (N * (Bo - Boi) + N * (Rsi - Rs) * Bg + m * N * Boi * (Bg / Bgi - 1))) * (1 - Swc) / (N * (1 + m) * Boi * (cw * Swc + cf))
For use in the code to find Np:
Np = (N * (Bo - Boi) + N * (Rsi - Rs) * Bg + m * N * Boi * (Bg / Bgi - 1) + N * (1 + m) * Boi * (Pi - Pres) * (cw * Swc + cf) / (1 - Swc) - (Wp * Bw - Wi * Bw - Gging * Bgi - We * Bw)) / (Bo + (Rp - Rs) * Bg)
Above the bubble point
where
Discussion
... most powerful tool for investigating reservoirs and understanding their performance ...— L.P. Dake [2]
... the safest technique in the business since it's minimum assumption route through the subject of reservoir engineering ...— L.P. Dake [2]
See also
Gas Material Balance
Gas Flowing Material Balance
Oil Flowing Material Balance
Nomenclature
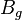 = gas formation volume factor at Pres, bbl/scf
= gas formation volume factor at Pres, bbl/scf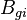 = initial gas formation volume factor, bbl/scf
= initial gas formation volume factor, bbl/scf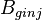 = injection gas formation volume factor at Pres, bbl/scf
= injection gas formation volume factor at Pres, bbl/scf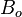 = oil formation volume factor at Pres, bbl/stb
= oil formation volume factor at Pres, bbl/stb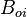 = initial oil formation volume factor, bbl/stb
= initial oil formation volume factor, bbl/stb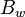 = water formation volume factor at Pres, bbl/stb
= water formation volume factor at Pres, bbl/stb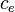 = effective system compressibility at Pres, 1/psia
= effective system compressibility at Pres, 1/psia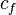 = formation compressibility at initial pressure and temperature, 1/psia
= formation compressibility at initial pressure and temperature, 1/psia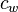 = water compressibility at Pres, 1/psia
= water compressibility at Pres, 1/psia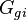 = gas injection volume, scf
= gas injection volume, scf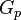 = gas cumulative production volume, scf
= gas cumulative production volume, scf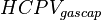 = initial gas cap hydrocarbon pore volume, bbl
= initial gas cap hydrocarbon pore volume, bbl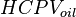 = initial oil hydrocarbon pore volume, bbl
= initial oil hydrocarbon pore volume, bbl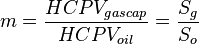 , initial gas cap oil leg ratio, dimensionless
, initial gas cap oil leg ratio, dimensionless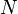 = stock tank oil initially in place, stb
= stock tank oil initially in place, stb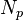 = oil cumulative production volume, stb
= oil cumulative production volume, stb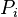 = initial reservoir pressure, psia
= initial reservoir pressure, psia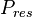 = average reservoir pressure, psia
= average reservoir pressure, psia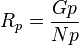 , cumulative GOR, scf/stb
, cumulative GOR, scf/stb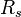 = solution oil-gas ratio, scf/bbl
= solution oil-gas ratio, scf/bbl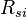 = initial solution oil-gas ratio, scf/bbl
= initial solution oil-gas ratio, scf/bbl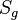 = initial gas saturation, fraction
= initial gas saturation, fraction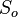 = initial oil saturation, fraction
= initial oil saturation, fraction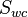 = connate water saturation, fraction
= connate water saturation, fraction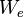 = water influx volume, stb
= water influx volume, stb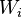 = water injection volume, stb
= water injection volume, stb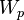 = water production volume, stb
= water production volume, stb
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Dake, L.P. (1978). Fundamentals of Reservoir Engineering. Amsterdam, Hetherlands: Elsevier Science. ISBN 0-444-41830-X.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 Dake, L.P. (1994). The Practice of Reservoir Engineering. Amsterdam, Hetherlands: Elsevier Science. ISBN 0-444-88538-2.