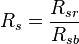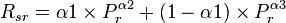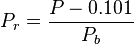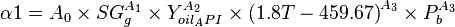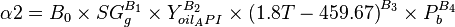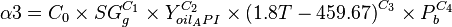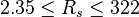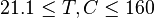Difference between revisions of "Velarde solution gas oil ratio correlation"
From wiki.pengtools.com
(→Brief) |
(→Velarde solution gas oil ratio correlation) |
||
| (25 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
__TOC__ | __TOC__ | ||
| − | == | + | == Velarde solution gas oil ratio correlation == |
| − | [[Velarde correlation]] is an empirical correlation for the '''solution gas oil ratio''' published in ''' | + | [[Velarde solution gas oil ratio correlation]] is an empirical correlation for the '''solution gas oil ratio''' published in '''1997'''. <ref name=Velarde /> |
| − | === Math & Physics | + | [[File:Valko McCain Bubble Point Pressure.png|thumb|right|400px|link=https://www.pengtools.com/pvtCalculator?paramsToken=de71e4cc29541ab2117e07408864410c|Velarde solution gas oil ratio correlation in the PVT Software]] |
| + | |||
| + | == Math & Physics == | ||
:<math>R_s = \frac{R_{sr}}{R_{sb}}</math> | :<math>R_s = \frac{R_{sr}}{R_{sb}}</math> | ||
| − | :<math>R_{sr} = \alpha1 \times P^{\alpha2}_r + (1 - \alpha1) \times P^{\alpha3}_r</math | + | :<math>R_{sr} = \alpha1 \times P^{\alpha2}_r + (1 - \alpha1) \times P^{\alpha3}_r</math> |
where: | where: | ||
| − | :<math>P_r = \frac{P}{ | + | :<math>P_r = \frac{P-0.101}{P_b}</math> |
| − | A0 = 1.8653e-4<br/> | + | :<math> \alpha1 = A_0 \times SG^{A_1}_g \times Y^{A_2}_{oil_API} \times {(1.8 T- 459.67)}^{A_3} \times P^{A_3}_b </math> |
| + | |||
| + | A0 = 1.8653e-4<ref name= PracticalPVT/><br/> | ||
A1 = 1.672608<br/> | A1 = 1.672608<br/> | ||
A2 = 0.929870<br/> | A2 = 0.929870<br/> | ||
| Line 20: | Line 24: | ||
A4 = 1.056052<br/> | A4 = 1.056052<br/> | ||
| − | :<math> \ | + | :<math>\alpha2 = B_0 \times SG^{B_1}_g \times Y^{B_2}_{oil_API} \times {(1.8 T - 459.67)}^{B_3} \times P^{B_4}_b</math> |
| − | B0 = 0.1004<br/> | + | B0 = 0.1004<ref name= PracticalPVT/><br/> |
B1 = -1.00475<br/> | B1 = -1.00475<br/> | ||
B2 = 0.337711<br/> | B2 = 0.337711<br/> | ||
| Line 28: | Line 32: | ||
B4 = 0.302065<br/> | B4 = 0.302065<br/> | ||
| − | :<math>\ | + | :<math>\alpha3 = C_0 \times SG^{C_1}_g \times Y^{C_2}_{oil_API} \times {(1.8 T - 459.67)}^{C_3} \times P^{C_4}_b</math> |
| − | C0 = 0.9167<br/> | + | C0 = 0.9167<ref name= PracticalPVT/><br/> |
C1 = -1.48548<br/> | C1 = -1.48548<br/> | ||
C2 = -0.164741<br/> | C2 = -0.164741<br/> | ||
| Line 36: | Line 40: | ||
C4 = 0.047094<br/> | C4 = 0.047094<br/> | ||
| − | :<math> | + | == Example. Calculation of the solution gas oil ratio == |
| + | Example source <ref name=DW/> | ||
| + | ===Input data=== | ||
| + | :<math>R_s</math> = 60 sm3/sm3 | ||
| + | :<math>SG_o</math> = 0.85 or 35 API | ||
| + | :<math>SG_g</math> = 0.75 | ||
| + | :<math>T</math> = 90C or 363K | ||
| + | :<math>P_b</math> = 11.65 MPa | ||
| + | Calculate solution gas oil ratio at p = 10 MPa? | ||
| − | === | + | ===Solution=== |
| − | + | Pr = 0.8493<br/> | |
| + | a1=0.1545<br/> | ||
| + | a2=1.8812<br/> | ||
| + | a3=0.5431<br/> | ||
| + | Rsr=0.8874<br/> | ||
| + | Rs=53.24 sm3/sm3<br/> | ||
| − | = | + | The solution is available in the online PVT calculator software at [https://www.pengtools.com/pvtCalculator?paramsToken=de71e4cc29541ab2117e07408864410c www.pengtools.com] |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | == Application range == | |
| − | :<math> | + | :<math> 2.35 \le R_s \le 322 </math> |
| − | :<math> | + | :<math> 0.754 \le SG_o \le 0.989 </math> |
| − | :<math> | + | :<math> 0.555 \le SG_g \le 1.245 </math> |
| − | :<math> P </math> = pressure, | + | :<math> 21.1 \le T, C \le 160 </math> |
| − | :<math> | + | |
| + | == Nomenclature == | ||
| + | :<math> API_{oil} </math> = oil specific gravity, °R | ||
| + | :<math> A_0..A_{4} </math> = coefficients | ||
| + | :<math> B_0..B_{4} </math> = coefficients | ||
| + | :<math> C_0..C_{4} </math> = coefficients | ||
| + | :<math> P </math> = pressure, MPa | ||
| + | :<math> P_b </math> = bubble point pressure, MPa | ||
| + | :<math> P_r </math> = reduced pressure, MPa | ||
| + | :<math> R_s </math> = solution oil gas ratio, sm3/sm3 | ||
| + | :<math> R_{rb} </math> = solution oil gas ratio at bubble point pressure, sm3/sm3 | ||
| + | :<math> R_{rs} </math> = reduced solution oil gas ratio, sm3/sm3 | ||
:<math> SG_g </math> = gas specific gravity, dimensionless | :<math> SG_g </math> = gas specific gravity, dimensionless | ||
| − | :<math> | + | :<math> SG_o </math> = oil specific gravity, dimensionless |
| − | :<math> | + | :<math> T </math> = temperature, °K |
| − | |||
| − | + | == References == | |
<references> | <references> | ||
<ref name=Velarde> | <ref name=Velarde> | ||
| Line 68: | Line 95: | ||
|url=https://www.onepetro.org/conference-paper/PETSOC-97-93 | |url=https://www.onepetro.org/conference-paper/PETSOC-97-93 | ||
|url-access=registration | |url-access=registration | ||
| + | }}</ref> | ||
| + | <ref name=PracticalPVT> | ||
| + | {{cite journal | ||
| + | |last1= Afanasyev |first1=Vitaliy | ||
| + | |last2= Moskvin |first2=Igor | ||
| + | |last3= Wolcott |first3=Ken | ||
| + | |last4= McCain |first4=W.D. | ||
| + | |title=Practical PVT Calculations for black oils | ||
| + | |journal=YUKOS publication | ||
| + | |date=2004 | ||
| + | }}</ref> | ||
| + | <ref name=DW> | ||
| + | {{cite book | ||
| + | |last1= Wolcott |first1=Don | ||
| + | |title=Applied Waterflood Field Development | ||
| + | |date=2009 | ||
| + | |publisher=Energy Tribune Publishing Inc | ||
| + | |place=Houston | ||
| + | |url=https://www.amazon.com/Applied-Waterflood-Field-Development-Wolcott/dp/0578023946/ref=sr_1_1?ie=UTF8&qid=1481788841&sr=8-1&keywords=Don+wolcott | ||
| + | |url-access=subscription | ||
}}</ref> | }}</ref> | ||
</references> | </references> | ||
| Line 73: | Line 120: | ||
[[Category:pengtools]] | [[Category:pengtools]] | ||
[[Category:PVT]] | [[Category:PVT]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | {{#seo: | ||
| + | |title=Velarde solution gas oil ratio GOR correlation | ||
| + | |titlemode= replace | ||
| + | |keywords=Velarde correlation | ||
| + | |description=Velarde correlation is an empirical correlation for the solution gas oil ratio (GOR) published in 1997. | ||
| + | }} | ||
Latest revision as of 08:54, 28 September 2020
Contents
Velarde solution gas oil ratio correlation
Velarde solution gas oil ratio correlation is an empirical correlation for the solution gas oil ratio published in 1997. [1]
Math & Physics
where:
A0 = 1.8653e-4[2]
A1 = 1.672608
A2 = 0.929870
A3 = 0.247235
A4 = 1.056052
B0 = 0.1004[2]
B1 = -1.00475
B2 = 0.337711
B3 = 0.132795
B4 = 0.302065
C0 = 0.9167[2]
C1 = -1.48548
C2 = -0.164741
C3 = -0.09133
C4 = 0.047094
Example. Calculation of the solution gas oil ratio
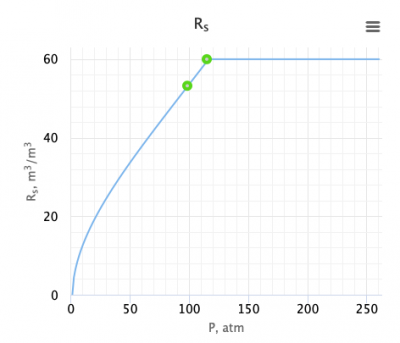
Example source [3]
Input data
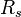 = 60 sm3/sm3
= 60 sm3/sm3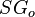 = 0.85 or 35 API
= 0.85 or 35 API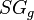 = 0.75
= 0.75 = 90C or 363K
= 90C or 363K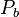 = 11.65 MPa
= 11.65 MPa
Calculate solution gas oil ratio at p = 10 MPa?
Solution
Pr = 0.8493
a1=0.1545
a2=1.8812
a3=0.5431
Rsr=0.8874
Rs=53.24 sm3/sm3
The solution is available in the online PVT calculator software at www.pengtools.com
Application range
Nomenclature
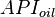 = oil specific gravity, °R
= oil specific gravity, °R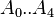 = coefficients
= coefficients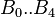 = coefficients
= coefficients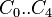 = coefficients
= coefficients = pressure, MPa
= pressure, MPa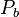 = bubble point pressure, MPa
= bubble point pressure, MPa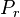 = reduced pressure, MPa
= reduced pressure, MPa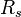 = solution oil gas ratio, sm3/sm3
= solution oil gas ratio, sm3/sm3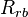 = solution oil gas ratio at bubble point pressure, sm3/sm3
= solution oil gas ratio at bubble point pressure, sm3/sm3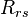 = reduced solution oil gas ratio, sm3/sm3
= reduced solution oil gas ratio, sm3/sm3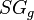 = gas specific gravity, dimensionless
= gas specific gravity, dimensionless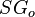 = oil specific gravity, dimensionless
= oil specific gravity, dimensionless = temperature, °K
= temperature, °K
References
- ↑
Velarde, J.; Blasingame, T. A.; McCain Jr., W. D. (1997). "Correlation of Black Oil Properties At Pressures Below Bubble Point Pressure - A New Approach"
 . Presented at the Annual Technical Meeting of CIM, Calgary, Alberta. Petroleum Society of Canada (PETSOC-97-93).
. Presented at the Annual Technical Meeting of CIM, Calgary, Alberta. Petroleum Society of Canada (PETSOC-97-93).
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 Afanasyev, Vitaliy; Moskvin, Igor; Wolcott, Ken; McCain, W.D. (2004). "Practical PVT Calculations for black oils". YUKOS publication.
- ↑
Wolcott, Don (2009). Applied Waterflood Field Development
 . Houston: Energy Tribune Publishing Inc.
. Houston: Energy Tribune Publishing Inc.