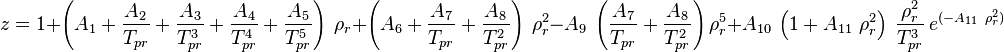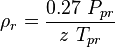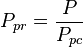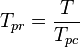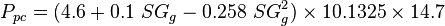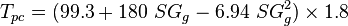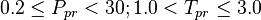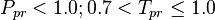Difference between revisions of "Dranchuk correlation"
From wiki.pengtools.com
(→Workflow) |
(→Math & Physics) |
||
| (13 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
__TOC__ | __TOC__ | ||
| − | == | + | == Dranchuk gas compressibility factor correlation == |
| − | [[Dranchuk correlation]] is the fitting equation of the classic '''Standing and Katz''' <ref name=Standing&Katz /> gas compressibility factor correlation. | + | [[Dranchuk correlation]] is the fitting equation of the classic '''Standing and Katz''' <ref name=Standing&Katz /> [[gas compressibility factor]] correlation. |
| − | + | == Math & Physics == | |
| − | + | :<math> z = 1 + | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | :<math> z = 1 | ||
\left(A_1 | \left(A_1 | ||
+\frac{A_2}{T_{pr}} | +\frac{A_2}{T_{pr}} | ||
| Line 29: | Line 17: | ||
+\frac{A_8}{T^2_{pr}} | +\frac{A_8}{T^2_{pr}} | ||
\right)\ \rho^2_r | \right)\ \rho^2_r | ||
| − | -A_9\ \left(\frac{A_7}{T_{pr}}+\frac{A_8}{T^2_{pr}}\right) | + | -A_9\ \left(\frac{A_7}{T_{pr}}+\frac{A_8}{T^2_{pr}}\right) \rho^5_r |
+A_{10}\ \left(1+A_{11}\ \rho^2_r\right)\ \frac{\rho^2_r}{T^3_{pr}} | +A_{10}\ \left(1+A_{11}\ \rho^2_r\right)\ \frac{\rho^2_r}{T^3_{pr}} | ||
\ e^{(-A_{11}\ \rho^2_r)} | \ e^{(-A_{11}\ \rho^2_r)} | ||
| Line 42: | Line 30: | ||
:<math> T_{pr} = \frac{T}{T_{pc}}</math> | :<math> T_{pr} = \frac{T}{T_{pc}}</math> | ||
| − | === Discussion | + | |
| − | Why [[Dranchuk correlation]]? | + | A1 = 0.3265<br/> |
| + | A2 = –1.0700<br/> | ||
| + | A3 = –0.5339<br/> | ||
| + | A4 = 0.01569<br/> | ||
| + | A5 = –0.05165<br/> | ||
| + | A6 = 0.5475<br/> | ||
| + | A7 = –0.7361<br/> | ||
| + | A8 = 0.1844<br/> | ||
| + | A9 = 0.1056<br/> | ||
| + | A10 = 0.6134<br/> | ||
| + | A11 = 0.7210<br/> | ||
| + | |||
| + | == Discussion == | ||
| + | Why the [[Dranchuk correlation]]? | ||
{{Quote| text = It's classics! | source = www.pengtools.com}} | {{Quote| text = It's classics! | source = www.pengtools.com}} | ||
| − | + | == Workflow == | |
To solve the [[Dranchuk correlation| Dranchuk]] equation use the iterative secant method. | To solve the [[Dranchuk correlation| Dranchuk]] equation use the iterative secant method. | ||
| − | To find the pseudo critical properties from the gas specific | + | To find the pseudo critical properties from the gas specific gravity <ref name=Standing&Katz />: |
| − | :<math> P_{pc} = 4.6+0.1\ SG_g-0.258\ SG^2_g</math> | + | :<math> P_{pc} = ( 4.6+0.1\ SG_g-0.258\ SG^2_g ) \times 10.1325 \times 14.7</math> |
| − | :<math> T_{pc} = 99.3+180\ SG_g-6.94\ SG^2_g</math> | + | :<math> T_{pc} = ( 99.3+180\ SG_g-6.94\ SG^2_g ) \times 1.8 </math> |
| − | + | == Application range == | |
| − | :<math> 0.2 \ | + | :<math> 0.2 \le P_{pr} < 30 ; 1.0 < T_{pr} \le 3.0 </math><ref name= Dranchuk/> |
| − | + | and | |
| − | === Nomenclature | + | :<math> P_{pr} < 1.0 ; 0.7 < T_{pr} \le 1.0</math><ref name= Dranchuk/> |
| + | |||
| + | == Nomenclature == | ||
:<math> A_1..A_{11} </math> = coefficients | :<math> A_1..A_{11} </math> = coefficients | ||
:<math> \rho_r </math> = reduced density, dimensionless | :<math> \rho_r </math> = reduced density, dimensionless | ||
| Line 74: | Line 77: | ||
:<math> z </math> = gas compressibility factor, dimensionless | :<math> z </math> = gas compressibility factor, dimensionless | ||
| − | + | == References == | |
<references> | <references> | ||
| Line 106: | Line 109: | ||
[[Category:pengtools]] | [[Category:pengtools]] | ||
[[Category:PVT]] | [[Category:PVT]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | {{#seo: | ||
| + | |title=Dranchuk gas compressibility factor correlation | ||
| + | |titlemode= replace | ||
| + | |keywords=Dranchuk correlation | ||
| + | |description=Dranchuk correlation is the fitting equation of the classic Standing and Katz gas compressibility factor correlation. | ||
| + | }} | ||
Latest revision as of 21:29, 23 November 2023
Contents
Dranchuk gas compressibility factor correlation
Dranchuk correlation is the fitting equation of the classic Standing and Katz [1] gas compressibility factor correlation.
Math & Physics
where:
A1 = 0.3265
A2 = –1.0700
A3 = –0.5339
A4 = 0.01569
A5 = –0.05165
A6 = 0.5475
A7 = –0.7361
A8 = 0.1844
A9 = 0.1056
A10 = 0.6134
A11 = 0.7210
Discussion
Why the Dranchuk correlation?
It's classics!— www.pengtools.com
Workflow
To solve the Dranchuk equation use the iterative secant method.
To find the pseudo critical properties from the gas specific gravity [1]:
Application range
and
Nomenclature
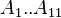 = coefficients
= coefficients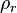 = reduced density, dimensionless
= reduced density, dimensionless = pressure, psia
= pressure, psia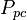 = pseudo critical pressure, psia
= pseudo critical pressure, psia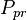 = pseudoreduced pressure, dimensionless
= pseudoreduced pressure, dimensionless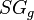 = gas specific gravity, dimensionless
= gas specific gravity, dimensionless = temperature, °R
= temperature, °R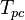 = pseudo critical temperature, °R
= pseudo critical temperature, °R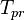 = pseudoreduced temperature, dimensionless
= pseudoreduced temperature, dimensionless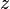 = gas compressibility factor, dimensionless
= gas compressibility factor, dimensionless
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Standing, M. B.; Katz, D. L. (December 1942). "Density of Natural Gases"
 . Transactions of the AIME. Society of Petroleum Engineers. 146 (SPE-942140-G).
. Transactions of the AIME. Society of Petroleum Engineers. 146 (SPE-942140-G).
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 Dranchuk, P. M.; Abou-Kassem, H. (July 1975). "Calculation of Z Factors For Natural Gases Using Equations of State"
 . The Journal of Canadian Petroleum. 14 (PETSOC-75-03-03).
. The Journal of Canadian Petroleum. 14 (PETSOC-75-03-03).