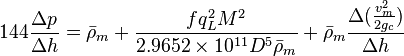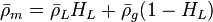Difference between revisions of "Hagedorn and Brown correlation"
From wiki.pengtools.com
| Line 7: | Line 7: | ||
The heart of the [[Hagedorn and Brown]] method is a correlation for the liquid holdup :<math>H_L</math>. | The heart of the [[Hagedorn and Brown]] method is a correlation for the liquid holdup :<math>H_L</math>. | ||
| + | == Math & Physics == | ||
The basic steady state flow equation is: | The basic steady state flow equation is: | ||
:<math> 144 \frac{\Delta p}{\Delta h} = \bar \rho_m + \frac{f q_L^2 M^2}{2.9652 \times 10^{11} D^5 \bar \rho_m} + \bar \rho_m \frac{\Delta{(\frac{v_m^2}{2g_c}})}{\Delta h}</math> | :<math> 144 \frac{\Delta p}{\Delta h} = \bar \rho_m + \frac{f q_L^2 M^2}{2.9652 \times 10^{11} D^5 \bar \rho_m} + \bar \rho_m \frac{\Delta{(\frac{v_m^2}{2g_c}})}{\Delta h}</math> | ||
Revision as of 14:48, 14 March 2017
Info
Hagedorn and Brown is an empirical two-phase flow correlation published in 1965.
It doesn't distinguish between the flow regimes.
The heart of the Hagedorn and Brown method is a correlation for the liquid holdup :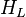 .
.
Math & Physics
The basic steady state flow equation is:
where
Workflow
For each pipe segment find: