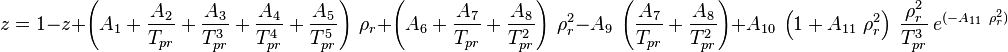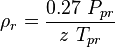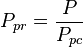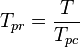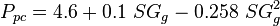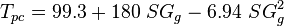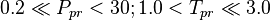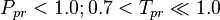Difference between revisions of "Dranchuk correlation"
From wiki.pengtools.com
(→Nomenclature) |
|||
| Line 58: | Line 58: | ||
=== Nomenclature === | === Nomenclature === | ||
| − | :<math> A_1..A_{11} </math> coefficients | + | :<math> A_1..A_{11} </math> = coefficients |
:<math> \rho_r </math> = reduced density, dimensionless | :<math> \rho_r </math> = reduced density, dimensionless | ||
| − | :<math> P </math> = | + | :<math> P </math> = pressure, psia |
:<math> P_{pc} </math> = pseudo critical pressure, psia | :<math> P_{pc} </math> = pseudo critical pressure, psia | ||
:<math> P_{pr} </math> = pseudoreduced pressure, dimensionless | :<math> P_{pr} </math> = pseudoreduced pressure, dimensionless | ||
Revision as of 13:32, 25 April 2017
Contents
Brief
Dranchuk correlation is the fitting equation of the classic Standing and Katz [1] gas compressibility factor correlation.
Math & Physics
A1 = 0.3265
A2 = –1.0700
A3 = –0.5339
A4 = 0.01569
A5 = –0.05165
A6 = 0.5475
A7 = –0.7361
A8 = 0.1844
A9 = 0.1056
A10 = 0.6134
A11 = 0.7210
where
Workflow
To solve the Dranchuk equation use the iterative secant method.
To find the pseudo critical properties given the gas specific gravity[1]:
Discussion
Application range
Nomenclature
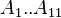 = coefficients
= coefficients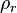 = reduced density, dimensionless
= reduced density, dimensionless = pressure, psia
= pressure, psia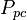 = pseudo critical pressure, psia
= pseudo critical pressure, psia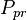 = pseudoreduced pressure, dimensionless
= pseudoreduced pressure, dimensionless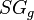 = gas specific gravity, dimensionless
= gas specific gravity, dimensionless = temperature, °R
= temperature, °R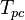 = pseudo critical temperature, °R
= pseudo critical temperature, °R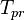 = pseudoreduced temperature, dimensionless
= pseudoreduced temperature, dimensionless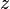 = gas compressibility factor, dimensionless
= gas compressibility factor, dimensionless
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Standing, M. B.; Katz, D. L. (December 1942). "Density of Natural Gases"
 . Transactions of the AIME. Society of Petroleum Engineers. 146 (SPE-942140-G).
. Transactions of the AIME. Society of Petroleum Engineers. 146 (SPE-942140-G).
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 Dranchuk, P. M.; Abou-Kassem, H. (July 1975). "Calculation of Z Factors For Natural Gases Using Equations of State"
 . The Journal of Canadian Petroleum. 14 (PETSOC-75-03-03).
. The Journal of Canadian Petroleum. 14 (PETSOC-75-03-03).