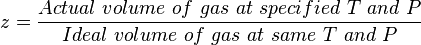Difference between revisions of "Gas compressibility factor"
From wiki.pengtools.com
| Line 5: | Line 5: | ||
:<math> z = \frac{Actual\ volume\ of\ gas\ at\ specified\ T\ and\ P}{Ideal\ volume\ of\ gas\ at\ same\ T\ and\ P} </math> <ref name=PEHvol1 /> | :<math> z = \frac{Actual\ volume\ of\ gas\ at\ specified\ T\ and\ P}{Ideal\ volume\ of\ gas\ at\ same\ T\ and\ P} </math> <ref name=PEHvol1 /> | ||
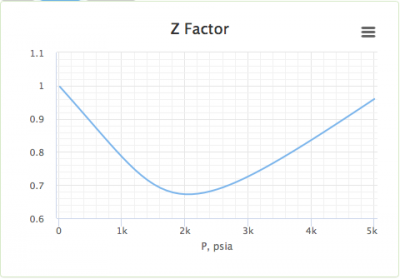
| − | [[File:zfactor.png|thumb|right|400px|link=https://www.pengtools.com/pvtCalculator|Z factor in the PVT | + | [[File:zfactor.png|thumb|right|400px|link=https://www.pengtools.com/pvtCalculator|Z factor in the PVT software at pengtools.com|right]] |
== Discussion == | == Discussion == | ||
Latest revision as of 11:59, 5 October 2020
Contents
Standing and Katz gas compressibility factor
gas compressibility factor is the ratio of the Real Gas volume to the Ideal Gas volume, which is a measure of the amount that the gas deviates from the perfect behavior.
Discussion
Dranchuk correlation is the default correlation for the gas compressibility factor in the PVT tool.
Nomenclature
 = Pressure, psia
= Pressure, psia = Temperature, °R
= Temperature, °R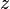 = Gas compressibility factor, dimensionless
= Gas compressibility factor, dimensionless
See also
Ideal Gas
Real Gas
gas compressibility factor
EOS
References
- ↑ Fanchi, John R. (2006). Petroleum Engineering Handbook, Volume I: General Engineering. 1. SPE. ISBN 978-1-55563-108-6.